Dental Waste Disposal Guidelines

Proper dental waste disposal is a critical yet often overlooked aspect of running a dental practice. As healthcare professionals, dentists are responsible to their patients, the environment, and the broader community. The diverse array of materials used in dental practices-from mercury-containing amalgam to potentially infectious items-requires careful handling and disposal to prevent harm to ecosystems and public health. In this blog, we’ll explore the essential guidelines for dental waste disposal, helping practitioners navigate the complex landscape of regulations and best practices. Whether you’re a seasoned dentist or just starting your practice, understanding and implementing proper waste management protocols is crucial for maintaining a safe, compliant, and environmentally responsible dental office.
Common Types of Dental Office Medical Waste
Several common types of dental waste require proper disposal. The main categories include:
- Amalgam Waste: This includes amalgam scrap, chair-side trap filters containing amalgam, vacuum pump filters, used amalgam capsules, and extracted teeth with amalgam fillings. Amalgam waste contains mercury and you must recycle it properly to prevent environmental contamination.
- Sharps Waste: This category includes needles, disposable scalpel blades, wires, and contaminated glass. These items must be disposed of in approved sharps containers.
- Biohazardous and Infectious Waste: This includes blood-soaked items like gauze, gloves, cotton balls, and extracted teeth.
- Hazardous Waste: This category encompasses chemicals, disinfectants, and sterilizing agents that may be ignitable, reactive, corrosive, or toxic.
- Pharmaceutical Waste: Unused, unwanted, or expired medications require proper disposal and can’t be flushed or thrown in regular trash.
- X-rays: This includes an X-ray fixer (high silver content) and unused X-ray developer (contains hydroquinone).
- Lead-Containing Waste: This includes lead foil from protective shields used in x-ray procedures.
Best Practices for Dental Waste Disposal
Implementing best practices for dental waste disposal ensures safety and compliance with regulations. Here are key guidelines:
Segregation
Proper segregation is the first step in effective waste management. Different types of waste should be separated at the source to facilitate safe disposal. Use color-coded bins and clearly label them to avoid confusion.
- General Waste: Black or clear bins
- Amalgam Waste: Use amalgam separators with at least 95% removal efficiency. Collect it separately for recycling and never dispose of it in regular trash, red bags, or down the drain.
- Infectious Waste: Yellow bins with biohazard symbols
- Sharps Waste: Red or yellow puncture-proof containers
- Chemical Waste: Appropriately labeled containers based on the chemical type
- Pharmaceutical Waste: Blue bins or containers
- Radioactive Waste: Lead-lined containers with radiation symbols.
Collection and Storage
Ensure that waste containers are accessible and located close to the point of waste generation. Please monitor and empty the containers regularly to prevent overflow. Store waste in a secure, designated area away from patient care areas and staff break rooms.
Treatment
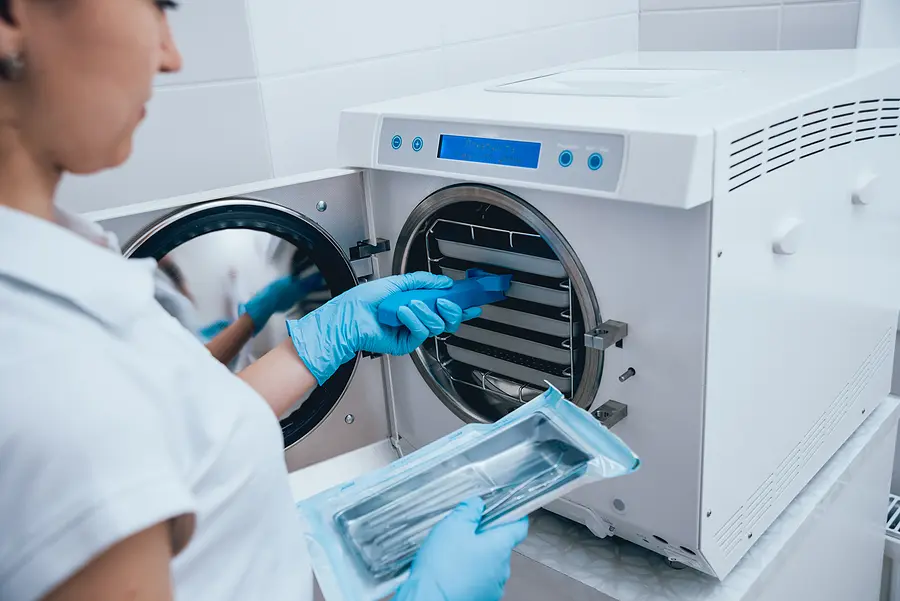

Infectious waste must be treated before disposal. Common methods include autoclaving (steam sterilization), chemical disinfection, and incineration. Each method has its advantages and regulatory guidelines, so choose the one that best fits your practice’s needs.
Disposal
After treatment, dispose of your dental waste according to local regulations. General waste can go to municipal landfills while disposing of treated infectious waste as non-hazardous waste. Seal your sharps containers and let authorized sharps disposal services handle them. Chemical and pharmaceutical waste should be disposed of through licensed hazardous waste disposal companies. Radioactive waste must follow specific guidelines set by regulatory authorities.
Compliance with Regulations
Compliance with regulations is essential for legal and ethical dental practice. Regulations may vary by country, state, or municipality, but some common guidelines include:
- OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration): OSHA provides standards in the United States for the handling and disposal of hazardous waste in dental practices.
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency): The EPA regulates the disposal of chemical and pharmaceutical waste to protect the environment.
- State and Local Regulations: Always check state and local regulations, as they may have specific requirements for dental waste disposal.
Training and Education
Regular training and education for all dental staff are crucial for effective waste management. Training should cover:
- Proper waste segregation and labeling
- Safe handling and disposal procedures
- Use of personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Emergency procedures for spills or exposure
Documentation and Record-Keeping
Maintain accurate records of waste disposal, including the type and quantity of waste, treatment methods, and disposal dates. Documentation helps in tracking compliance and can be crucial during inspections by regulatory authorities.
Environmental Responsibility
Beyond regulatory compliance, dental practices have a responsibility to minimize their environmental impact. Implementing eco-friendly practices such as reducing waste generation, recycling, and using biodegradable products can contribute to environmental sustainability.
Improve Your Dental Waste Disposal Today
By implementing these dental waste disposal guidelines, dental practices can ensure proper waste disposal, maintain compliance with regulations, and minimize their environmental impact. Medical Waste Pros can connect your dental practice with safe and effective dental waste disposal services in your area. To start, fill out the form, or give us a call at (888) 755-6370 for free quotes on services near you!










